We will need to add a function (calcMarginalLikelihood) and a couple of variables (_steppingstone and _ss_alpha) to strom.hpp to hold settings that allow users to specify that they would like to carry out a steppingstone analysis rather than an ordinary MCMC analysis.
class Strom {
public:
Strom();
~Strom();
void clear();
void processCommandLineOptions(int argc, const char * argv[]);
void run();
private:
bool processAssignmentString(Model::SharedPtr m, const std::string & which, const std::string & definition);
void handleAssignmentStrings(Model::SharedPtr m, const boost::program_options::variables_map & vm, std::string label, const std::vector<std::string> & definitions, std::string default_definition);
bool splitAssignmentString(const std::string & definition, std::vector<std::string> & vector_of_subset_names, std::vector<double> & vector_of_values);
void sample(unsigned iter, Chain & chain);
void readData();
void readTrees();
void showPartitionInfo();
void showBeagleInfo();
void showMCMCInfo();
void calcHeatingPowers();
<span style="color:#0000ff"><strong>void calcMarginalLikelihood() const;</strong></span>
void initChains();
void startTuningChains();
void stopTuningChains();
void stepChains(unsigned iteration, bool sampling);
void swapChains();
void stopChains();
void swapSummary() const;
void showChainTuningInfo() const;
double _expected_log_likelihood;
double _topo_prior_C;
bool _allow_polytomies;
bool _resolution_class_prior;
std::string _data_file_name;
std::string _tree_file_name;
Partition::SharedPtr _partition;
Data::SharedPtr _data;
std::vector<Likelihood::SharedPtr> _likelihoods;
TreeSummary::SharedPtr _tree_summary;
Lot::SharedPtr _lot;
unsigned _random_seed;
unsigned _num_iter;
unsigned _print_freq;
unsigned _sample_freq;
unsigned _num_burnin_iter;
bool _using_stored_data;
bool _use_gpu;
<span style="color:#0000ff"><strong>bool _steppingstone;</strong></span>
<span style="color:#0000ff"><strong>double _ss_alpha;</strong></span>
bool _ambig_missing;
unsigned _num_chains;
double _heating_lambda;
std::vector<Chain> _chains;
std::vector<double> _heating_powers;
std::vector<unsigned> _swaps;
bool _use_underflow_scaling;
static std::string _program_name;
static unsigned _major_version;
static unsigned _minor_version;
OutputManager::SharedPtr _output_manager;
};
Initialize the new variables in the clear function:
inline void Strom::clear() {
_data_file_name = "";
_tree_file_name = "";
_tree_summary = nullptr;
_partition.reset(new Partition());
_use_gpu = true;
<span style="color:#0000ff"><strong>_steppingstone = false;</strong></span>
<span style="color:#0000ff"><strong>_ss_alpha = 0.25;</strong></span>
_ambig_missing = true;
_expected_log_likelihood = 0.0;
_data = nullptr;
_use_underflow_scaling = false;
_lot = nullptr;
_random_seed = 1;
_num_iter = 1000;
_print_freq = 1;
_sample_freq = 1;
_output_manager = nullptr;
_topo_prior_C = 1.0;
_allow_polytomies = true;
_resolution_class_prior = true;
_using_stored_data = true;
_likelihoods.clear();
_num_burnin_iter = 1000;
_heating_lambda = 0.5;
_num_chains = 1;
_chains.resize(0);
_heating_powers.resize(0);
_swaps.resize(0);
}
Adding program options
Create program options that the user can access in the processCommandLineOptions function:
inline void Strom::processCommandLineOptions(int argc, const char * argv[]) {
std::vector<std::string> partition_statefreq;
std::vector<std::string> partition_rmatrix;
std::vector<std::string> partition_omega;
std::vector<std::string> partition_ratevar;
std::vector<std::string> partition_pinvar;
std::vector<std::string> partition_ncateg;
std::vector<std::string> partition_subsets;
std::vector<std::string> partition_relrates;
std::vector<std::string> partition_tree;
boost::program_options::variables_map vm;
boost::program_options::options_description desc("Allowed options");
desc.add_options()
("help,h", "produce help message")
("version,v", "show program version")
("seed,z", boost::program_options::value(&_random_seed)->default_value(1), "pseudorandom number seed")
("niter,n", boost::program_options::value(&_num_iter)->default_value(1000), "number of MCMC iterations")
("printfreq", boost::program_options::value(&_print_freq)->default_value(1), "skip this many iterations before reporting progress")
("samplefreq", boost::program_options::value(&_sample_freq)->default_value(1), "skip this many iterations before sampling next")
("datafile,d", boost::program_options::value(&_data_file_name)->required(), "name of a data file in NEXUS format")
("treefile,t", boost::program_options::value(&_tree_file_name)->required(), "name of a tree file in NEXUS format")
("subset", boost::program_options::value(&partition_subsets), "a string defining a partition subset, e.g. 'first:1-1234\3' or 'default[codon:standard]:1-3702'")
("ncateg,c", boost::program_options::value(&partition_ncateg), "number of categories in the discrete Gamma rate heterogeneity model")
("statefreq", boost::program_options::value(&partition_statefreq), "a string defining state frequencies for one or more data subsets, e.g. 'first,second:0.1,0.2,0.3,0.4'")
("omega", boost::program_options::value(&partition_omega), "a string defining the nonsynonymous/synonymous rate ratio omega for one or more data subsets, e.g. 'first,second:0.1'")
("rmatrix", boost::program_options::value(&partition_rmatrix), "a string defining the rmatrix for one or more data subsets, e.g. 'first,second:1,2,1,1,2,1'")
("ratevar", boost::program_options::value(&partition_ratevar), "a string defining the among-site rate variance for one or more data subsets, e.g. 'first,second:2.5'")
("pinvar", boost::program_options::value(&partition_pinvar), "a string defining the proportion of invariable sites for one or more data subsets, e.g. 'first,second:0.2'")
("relrate", boost::program_options::value(&partition_relrates), "a string defining the (unnormalized) relative rates for all data subsets (e.g. 'default:3,1,6').")
("tree", boost::program_options::value(&partition_tree), "the index of the tree in the tree file (first tree has index = 1)")
("topopriorC", boost::program_options::value(&_topo_prior_C)->default_value(1.0), "topology prior C: tree (or resolution class) with m internal nodes has probability C time greater than tree (or resolution class) with m+1 internal nodes.")
("allowpolytomies", boost::program_options::value(&_allow_polytomies)->default_value(true), "yes or no; if yes, then topopriorC and polytomyprior are used, otherwise topopriorC and polytomyprior are ignored")
("resclassprior", boost::program_options::value(&_resolution_class_prior)->default_value(true), "if yes, topologypriorC will apply to resolution classes; if no, topologypriorC will apply to individual tree topologies")
("expectedLnL", boost::program_options::value(&_expected_log_likelihood)->default_value(0.0), "log likelihood expected")
("nchains", boost::program_options::value(&_num_chains)->default_value(1), "number of chains")
("heatfactor", boost::program_options::value(&_heating_lambda)->default_value(0.5), "determines how hot the heated chains are")
("burnin", boost::program_options::value(&_num_burnin_iter)->default_value(100), "number of iterations used to burn in chains")
("usedata", boost::program_options::value(&_using_stored_data)->default_value(true), "use the stored data in calculating likelihoods (specify no to explore the prior)")
("gpu", boost::program_options::value(&_use_gpu)->default_value(true), "use GPU if available")
("ambigmissing", boost::program_options::value(&_ambig_missing)->default_value(true), "treat all ambiguities as missing data")
("underflowscaling", boost::program_options::value(&_use_underflow_scaling)->default_value(true), "scale site-likelihoods to prevent underflow (slower but safer)")
<span style="color:#0000ff"><strong>("steppingstone", boost::program_options::value(&_steppingstone)->default_value(false), "use heated chains to compute marginal likelihood with the steppingstone method")</strong></span>
<span style="color:#0000ff"><strong>("ssalpha", boost::program_options::value(&_ss_alpha)->default_value(0.25), "determines how bunched steppingstone chain powers are toward the prior: chain k of K total chains has power (k/K)^{1/ssalpha}")</strong></span>
;
Modifying the sample function
Add a conditional to the sample function to account for the fact that the chains are doing something quite differently under steppingstone than under normal MCMC sampling:
inline void Strom::sample(unsigned iteration, Chain & chain) {
<span style="color:#0000ff"><strong>if (_steppingstone) {</strong></span>
<span style="color:#0000ff"><strong>bool time_to_sample = (bool)(iteration % _sample_freq == 0);</strong></span>
<span style="color:#0000ff"><strong>if (time_to_sample && iteration > 0) {</strong></span>
<span style="color:#0000ff"><strong>chain.storeLogLikelihood();</strong></span>
<span style="color:#0000ff"><strong>}</strong></span>
<span style="color:#0000ff"><strong></strong></span>
<span style="color:#0000ff"><strong>assert(_heating_powers.size() > 0);</strong></span>
<span style="color:#0000ff"><strong>double largest_power = *(_heating_powers.rbegin());</strong></span>
<span style="color:#0000ff"><strong>if (chain.getHeatingPower() != largest_power)</strong></span>
<span style="color:#0000ff"><strong>return;</strong></span>
<span style="color:#0000ff"><strong></strong></span>
<span style="color:#0000ff"><strong>bool time_to_report = (bool)(iteration % _print_freq == 0);</strong></span>
<span style="color:#0000ff"><strong>if (time_to_report) {</strong></span>
<span style="color:#0000ff"><strong>double logLike = chain.getLogLikelihood();</strong></span>
<span style="color:#0000ff"><strong>double logPrior = chain.calcLogJointPrior();</strong></span>
<span style="color:#0000ff"><strong>double TL = chain.getTreeManip()->calcTreeLength();</strong></span>
<span style="color:#0000ff"><strong>unsigned m = chain.getTreeManip()->calcResolutionClass();</strong></span>
<span style="color:#0000ff"><strong>if (time_to_report) {</strong></span>
<span style="color:#0000ff"><strong>if (logPrior == Updater::getLogZero())</strong></span>
<span style="color:#0000ff"><strong>_output_manager->outputConsole(boost::str(boost::format("%12d %12d %12.5f %12s %12.5f") % iteration % m % logLike % "-infinity" % TL));</strong></span>
<span style="color:#0000ff"><strong>else</strong></span>
<span style="color:#0000ff"><strong>_output_manager->outputConsole(boost::str(boost::format("%12d %12d %12.5f %12.5f %12.5f") % iteration % m % logLike % logPrior % TL));</strong></span>
<span style="color:#0000ff"><strong>}</strong></span>
<span style="color:#0000ff"><strong>}</strong></span>
<span style="color:#0000ff"><strong>}</strong></span>
<span style="color:#0000ff"><strong>else {</strong></span>
if (chain.getHeatingPower() < 1.0)
return;
bool time_to_sample = (bool)(iteration % _sample_freq == 0);
bool time_to_report = (bool)(iteration % _print_freq == 0);
if (time_to_sample || time_to_report) {
double logLike = chain.getLogLikelihood();
double logPrior = chain.calcLogJointPrior();
double TL = chain.getTreeManip()->calcTreeLength();
unsigned m = chain.getTreeManip()->calcResolutionClass();
if (time_to_report) {
if (logPrior == Updater::getLogZero())
_output_manager->outputConsole(boost::str(boost::format("%12d %12d %12.5f %12s %12.5f") % iteration % m % logLike % "-infinity" % TL));
else
_output_manager->outputConsole(boost::str(boost::format("%12d %12d %12.5f %12.5f %12.5f") % iteration % m % logLike % logPrior % TL));
}
if (time_to_sample) {
_output_manager->outputTree(iteration, chain.getTreeManip());
_output_manager->outputParameters(iteration, logLike, logPrior, TL, m, chain.getModel());
}
}
<span style="color:#0000ff"><strong>}</strong></span>
}
You will note that the steppingstone section is almost the same as the non-steppingstone section, but there are some key differences. Ordinarily (i.e. when we are not doing steppingstone), we only produce a progress report for the cold chain. That explains why we return from the function early if the heating power is less than 1. Under steppingstone, it is arbitrary which chain we use when reporting progress, so I’ve chosen here to report progress for the chain with the largest power, which is the final entry in the _heating_powers vector.
You’ll notice that, in the steppingstone section, I’ve also left out code to save parameter values to the sampled parameters and sampled trees files. Samples from these chains have no use except to estimate the marginal likelihood.
Finally, at the beginning of the steppingstone section, a new function storeLogLikelihood is called for each chain if it is time to sample. This function, as you’ll see when you create it, just stores the current log-likelihood in a vector named _ss_loglikes, which is a data member of the Chain class.
Modifying the calcHeatingPowers function
In the calcHeatingPowers function, we need to setup the chain powers differently for steppingstone than for ordinary Metropolis-coupled MCMC. In MCMCMC, it is not wise to let the chain powers get too small. For example, if the chain power were set to zero, the chain would explore the prior and would almost never serve as a useful scout for the cold chain. On the other hand, the chain powers used in steppingstone are concentrated toward the prior end of the spectrum. The reason for this is best explained graphically. Returning to our coin-flipping example, compare the power posterior distributions for evenly-spaced powers (left) to the power posterior distributions for powers concentrated toward the prior end of the spectrum (right).
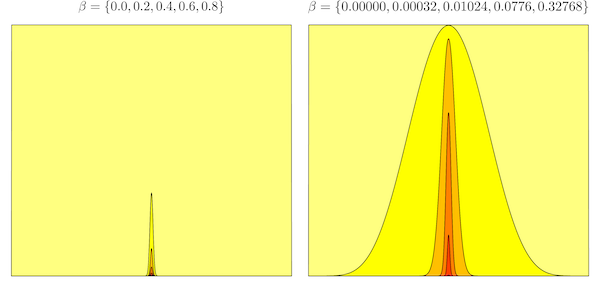 As you can see, evenly-spaced powers do not result in homogeneous ratios between adjacent distributions. It is as if the steppingstones placed to help cross a stream involved a really big first jump and then really tiny jumps thereafter. Bunching powers close to the prior results in ratios that are more even and thus more easily and accurately estimated.
As you can see, evenly-spaced powers do not result in homogeneous ratios between adjacent distributions. It is as if the steppingstones placed to help cross a stream involved a really big first jump and then really tiny jumps thereafter. Bunching powers close to the prior results in ratios that are more even and thus more easily and accurately estimated.
The degree to which the heating powers are pushed towards 0.0 is determined by the _ss_alpha setting. The code highlighted below allocates heating powers for steppingstone based on the number of chains specified and the value of _ss_alpha. Note that if _ss_alpha equals 1, then the powers will be evenly spaced between 0 and 1 (but note that power equal to 1 is never used). If _ss_alpha is less than 1, then the nominal (equally spaced) power is raised to the value 1/_ss_alpha. An example is provided in the comments for K=5 chains and _ss_alpha = 0.25.
inline void Strom::calcHeatingPowers() {
<span style="color:#0000ff"><strong>if (_steppingstone) {</strong></span>
<span style="color:#0000ff"><strong>// Specify chain heating power for steppingstone</strong></span>
<span style="color:#0000ff"><strong>// For K = 5 chains and alpha = 0.25 (1/alpha = 4):</strong></span>
<span style="color:#0000ff"><strong>// k chain power</strong></span>
<span style="color:#0000ff"><strong>// ---------------------</strong></span>
<span style="color:#0000ff"><strong>// 0 (0/5)^4 = 0.0000 <-- prior</strong></span>
<span style="color:#0000ff"><strong>// 1 (1/5)^4 = 0.0016</strong></span>
<span style="color:#0000ff"><strong>// 2 (2/5)^4 = 0.0256</strong></span>
<span style="color:#0000ff"><strong>// 3 (3/5)^4 = 0.1296</strong></span>
<span style="color:#0000ff"><strong>// 4 (4/5)^4 = 0.4096</strong></span>
<span style="color:#0000ff"><strong>// 5 (5/5)^4 = 1.0000 <-- posterior not used</strong></span>
<span style="color:#0000ff"><strong>double inv_alpha = 1.0/_ss_alpha;</strong></span>
<span style="color:#0000ff"><strong>double k = 0.0;</strong></span>
<span style="color:#0000ff"><strong>double K = (double)_heating_powers.size();</strong></span>
<span style="color:#0000ff"><strong>for (auto & h : _heating_powers) {</strong></span>
<span style="color:#0000ff"><strong>h = pow(k++/K, inv_alpha);</strong></span>
<span style="color:#0000ff"><strong>}</strong></span>
<span style="color:#0000ff"><strong>}</strong></span>
<span style="color:#0000ff"><strong>else {</strong></span>
// Specify chain heating power (e.g. _heating_lambda = 0.2)
// chain_index power
// 0 1.000 = 1/(1 + 0.2*0)
// 1 0.833 = 1/(1 + 0.2*1)
// 2 0.714 = 1/(1 + 0.2*2)
// 3 0.625 = 1/(1 + 0.2*3)
unsigned i = 0;
for (auto & h : _heating_powers) {
h = 1.0/(1.0 + _heating_lambda*i++);
}
<span style="color:#0000ff"><strong>}</strong></span>
}
Adding the calcMarginalLikelihood function
Once all heated chains have finished, the calcMarginalLikelihood function can be called to do the final computation.
inline void Strom::calcMarginalLikelihood() const {
if (_steppingstone) {
// Calculate the log ratio for each steppingstone
std::vector<std::pair<double, double> > log_ratio;
for (auto & c : _chains) {
log_ratio.push_back(std::make_pair(c.getHeatingPower(), c.calcLogSteppingstoneRatio()));
}
// Sort log_ratio vector from lowest to highest power
std::sort(log_ratio.begin(), log_ratio.end());
_output_manager->outputConsole("\nSteppingstone results:");
_output_manager->outputConsole(boost::str(boost::format("%20s %20s %20s") % "beta" % "log(ratio)" % "cumulative"));
double log_marginal_likelihood = 0.0;
for (auto p : log_ratio) {
double beta = p.first;
double logratio = p.second;
log_marginal_likelihood += logratio;
_output_manager->outputConsole(boost::str(boost::format("%20.5f %20.5f %20.5f") % beta % logratio % log_marginal_likelihood));
}
_output_manager->outputConsole(boost::str(boost::format("\nlog(marginal likelihood) = %.5f") % log_marginal_likelihood));
}
}
This function first creates a vector of pairs in which the first element is the heating power of the chain and the second element is the steppingstone ratio calculated for that chain. The next step is to sort this vector so that elements are in order of heating power. This sorting is purely cosmetic: sorting causes the output to have increasing chain powers and not a random ordering.
I mentioned in the introduction that the estimated marginal likelihood is simply the product of the ratios calculated from each steppingstone power posterior distribution. On the log scale, this amounts to adding up the log ratios computed by each chain. This simple summation is performed in the last section of this function while outputting the heating powers and the estimated log ratios from each chain.
Miscellany
Before moving on to making necessary modifications and additions to the Chain class, I want to finish up work on the Strom class.
Because it makes no sense to swap chains during steppingstone, we need to be sure to turn off chain swapping if steppingstone is being performed. In the swapChains function, this is as simple as changing if (_num_chains == 1) return; to if (_num_chains == 1 || _steppingstone) return; in the first statement inside the function body:
inline void Strom::swapChains() {
<span style="color:#0000ff"><strong>//if (_num_chains == 1)</strong></span>
<span style="color:#0000ff"><strong>if (_num_chains == 1 || _steppingstone)</strong></span>
return;
// Select two chains at random to swap
// If _num_chains = 3...
// i j = (i + 1 + randint(0,1)) % _num_chains
// ---------------------------------------------
// 0 1 = (0 + 1 + 0 ) % 3
// 2 = (0 + 1 + 1 ) % 3
// ---------------------------------------------
// 1 2 = (1 + 1 + 0 ) % 3
// 0 = (1 + 1 + 1 ) % 3
// ---------------------------------------------
// 2 0 = (2 + 1 + 0 ) % 3
// 1 = (2 + 1 + 1 ) % 3
// ---------------------------------------------
unsigned i = (unsigned)_lot->randint(0, _num_chains-1);
unsigned j = i + 1 + (unsigned)_lot->randint(0, _num_chains-2);
j %= _num_chains;
assert(i != j && i >=0 && i < _num_chains && j >= 0 && j < _num_chains);
// Determine upper and lower triangle cells in _swaps vector
unsigned smaller = _num_chains;
unsigned larger = _num_chains;
double index_i = _chains[i].getChainIndex();
double index_j = _chains[j].getChainIndex();
if (index_i < index_j) {
smaller = index_i;
larger = index_j;
}
else {
smaller = index_j;
larger = index_i;
}
unsigned upper = smaller*_num_chains + larger;
unsigned lower = larger*_num_chains + smaller;
_swaps[upper]++;
// Propose swap of chains i and j
// Proposed state swap will be successful if a uniform random deviate is less than R, where
// R = Ri * Rj = (Pi(j) / Pi(i)) * (Pj(i) / Pj(j))
// Chain i: power = a, kernel = pi
// Chain j: power = b, kernel = pj
// pj^a pi^b
// Ri = ---- Rj = ----
// pi^a pj^b
// log R = (a-b) [log(pj) - log(pi)]
double heat_i = _chains[i].getHeatingPower();
double log_kernel_i = _chains[i].calcLogLikelihood() + _chains[i].calcLogJointPrior();
double heat_j = _chains[j].getHeatingPower();
double log_kernel_j = _chains[j].calcLogLikelihood() + _chains[j].calcLogJointPrior();
double logR = (heat_i - heat_j)*(log_kernel_j - log_kernel_i);
double logu = _lot->logUniform();
if (logu < logR) {
// accept swap
_swaps[lower]++;
_chains[j].setHeatingPower(heat_i);
_chains[i].setHeatingPower(heat_j);
_chains[j].setChainIndex(index_i);
_chains[i].setChainIndex(index_j);
std::vector<double> lambdas_i = _chains[i].getLambdas();
std::vector<double> lambdas_j = _chains[j].getLambdas();
_chains[i].setLambdas(lambdas_j);
_chains[j].setLambdas(lambdas_i);
}
}
Make the same kind of modification to the swapSummary function:
inline void Strom::swapSummary() const {
<span style="color:#0000ff"><strong>//if (_num_chains > 1) {</strong></span>
<span style="color:#0000ff"><strong>if (_num_chains > 1 && !_steppingstone) {</strong></span>
unsigned i, j;
std::cout << "\nSwap summary (upper triangle = no. attempted swaps; lower triangle = no. successful swaps):" << std::endl;
// column headers
std::cout << boost::str(boost::format("%12s") % " ");
for (i = 0; i < _num_chains; ++i)
std::cout << boost::str(boost::format(" %12d") % i);
std::cout << std::endl;
// top line
std::cout << boost::str(boost::format("%12s") % "------------");
for (i = 0; i < _num_chains; ++i)
std::cout << boost::str(boost::format("-%12s") % "------------");
std::cout << std::endl;
// table proper
for (i = 0; i < _num_chains; ++i) {
std::cout << boost::str(boost::format("%12d") % i);
for (j = 0; j < _num_chains; ++j) {
if (i == j)
std::cout << boost::str(boost::format(" %12s") % "---");
else
std::cout << boost::str(boost::format(" %12.5f") % _swaps[i*_num_chains + j]);
}
std::cout << std::endl;
}
// bottom line
std::cout << boost::str(boost::format("%12s") % "------------");
for (i = 0; i < _num_chains; ++i)
std::cout << boost::str(boost::format("-%12s") % "------------");
std::cout << std::endl;
}
}
In order to calculate their particular steppingstone ratio, each chain must know not only the heating power that it is using but also the heating power of the power posterior distribution that is nested just inside it. The chains are told not only their heating power but this “next heating power” in the initChains function:
inline void Strom::initChains() {
//...
// Create _num_chains chains
_chains.resize(_num_chains);
// Create _num_chains by _num_chains swap matrix
_swaps.assign(_num_chains*_num_chains, 0);
// Create heating power vector
_heating_powers.assign(_num_chains, 1.0);
calcHeatingPowers();
// Initialize chains
for (unsigned chain_index = 0; chain_index < _num_chains; ++chain_index) {
auto & c = _chains[chain_index];
auto likelihood = _likelihoods[chain_index];
auto m = likelihood->getModel();
// Finish setting up models
m->setTopologyPriorOptions(_allow_polytomies, _resolution_class_prior, _topo_prior_C);
m->setSubsetNumPatterns(_data->calcNumPatternsVect());
m->setSubsetSizes(_partition->calcSubsetSizes());
m->activate();
if (chain_index == 0)
std::cout << "\n" << m->describeModel() << std::endl;
else
m->describeModel();
// Finish setting up likelihoods
likelihood->setData(_data);
likelihood->useUnderflowScaling(_use_underflow_scaling);
likelihood->initBeagleLib();
likelihood->useStoredData(_using_stored_data);
// Build list of updaters, one for each free parameter in the model
unsigned num_free_parameters = c.createUpdaters(m, _lot, likelihood);
if (num_free_parameters == 0)
throw XStrom("MCMC skipped because there are no free parameters in the model");
// Tell the chain that it should adapt its updators (at least initially)
c.startTuning();
// Set heating power to precalculated value
c.setChainIndex(chain_index);
c.setHeatingPower(_heating_powers[chain_index]);
<span style="color:#0000ff"><strong>if (_steppingstone) {</strong></span>
<span style="color:#0000ff"><strong>if (chain_index == _num_chains - 1)</strong></span>
<span style="color:#0000ff"><strong>c.setNextHeatingPower(1.0);</strong></span>
<span style="color:#0000ff"><strong>else</strong></span>
<span style="color:#0000ff"><strong>c.setNextHeatingPower(_heating_powers[chain_index + 1]);</strong></span>
<span style="color:#0000ff"><strong>}</strong></span>
// Give the chain a starting tree
std::string newick = _tree_summary->getNewick(m->getTreeIndex());
c.setTreeFromNewick(newick);
// Print headers in output files and make sure each updator has its starting value
c.start();
}
}
The last modifications we need to make in the Strom class are to the run function: (1) add the calcMarginalLikelihood call and (2) avoid opening the parameter or tree output files if steppingstone is in progress. Note that calcMarginalLikelihood is a no-op (i.e. no-operation, nothing done) if we are not currently carrying out steppingstone.
inline void Strom::run() {
std::cout << "Starting..." << std::endl;
std::cout << "Current working directory: " << boost::filesystem::current_path() << std::endl;
try {
readData();
readTrees();
showPartitionInfo();
// Create a Lot object that generates (pseudo)random numbers
_lot = Lot::SharedPtr(new Lot);
_lot->setSeed(_random_seed);
// Create Chain objects
initChains();
showBeagleInfo();
showMCMCInfo();
// Create an output manager and open output files
_output_manager.reset(new OutputManager);
_output_manager->outputConsole(boost::str(boost::format("\n%12s %12s %12s %12s %12s") % "iteration" % "m" % "logLike" % "logPrior" % "TL"));
<span style="color:#0000ff"><strong>if (!_steppingstone) {</strong></span>
_output_manager->openTreeFile("trees.tre", _data);
_output_manager->openParameterFile("params.txt", _chains[0].getModel());
<span style="color:#0000ff"><strong>}</strong></span>
sample(0, _chains[0]);
// Burn-in the chains
startTuningChains();
for (unsigned iteration = 1; iteration <= _num_burnin_iter; ++iteration) {
stepChains(iteration, false);
swapChains();
}
stopTuningChains();
// Sample the chains
for (unsigned iteration = 1; iteration <= _num_iter; ++iteration) {
stepChains(iteration, true);
swapChains();
}
showChainTuningInfo();
stopChains();
// Create swap summary
swapSummary();
<span style="color:#0000ff"><strong>// Estimate the marginal likelihood if doing steppingstone</strong></span>
<span style="color:#0000ff"><strong>calcMarginalLikelihood();</strong></span>
// Close output files
<span style="color:#0000ff"><strong>if (!_steppingstone) {</strong></span>
_output_manager->closeTreeFile();
_output_manager->closeParameterFile();
<span style="color:#0000ff"><strong>}</strong></span>
}
catch (XStrom & x) {
std::cerr << "Strom encountered a problem:\n " << x.what() << std::endl;
}
std::cout << "\nFinished!" << std::endl;
}